A Guide To Customer Payment Modes
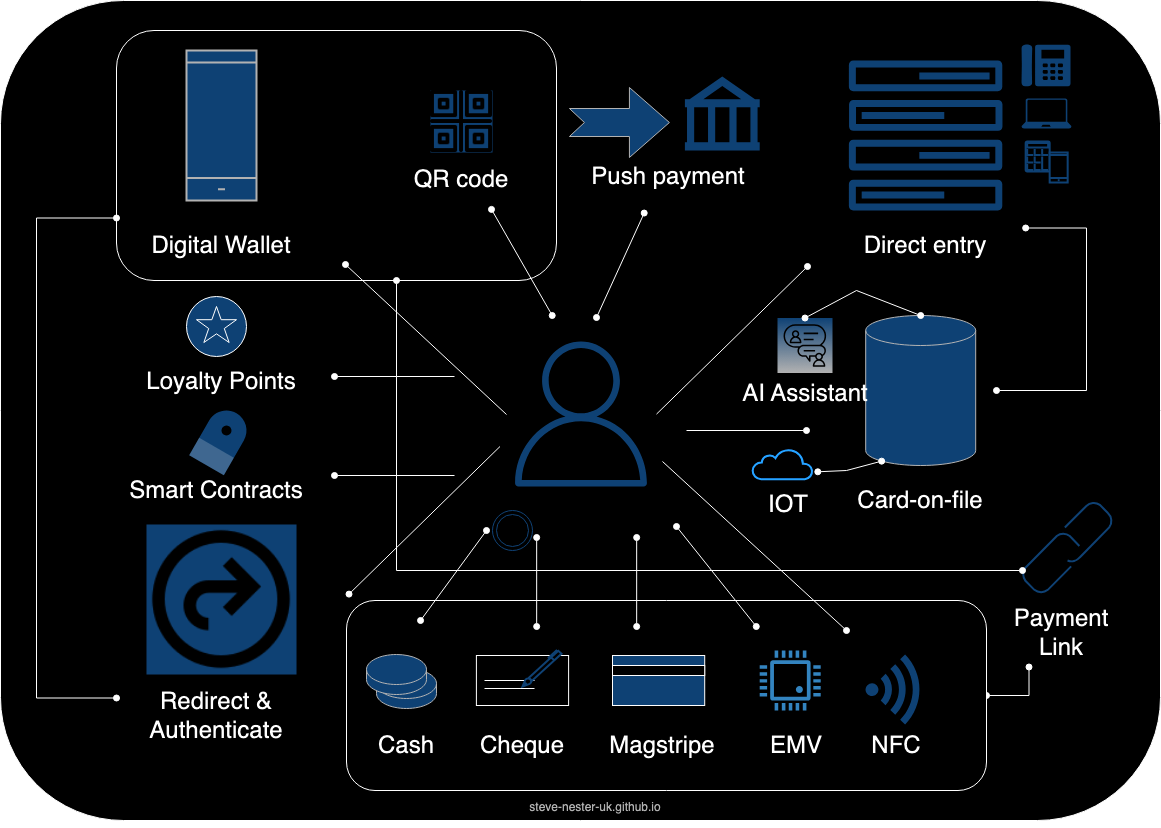
Here are the various ways a customer can pay, i.e. customer payment modes. Not to be confused with payment methods! I've managed to think of 13 below but I have a feeling this list isn't comprehensive so please do let me know what other I've missed.
- Direct entry
- Card-on-file
- NFC
- EMV
- Magstripe
- Cheque
- Cash
- Redirect
- Loyalty Points
- Digital Wallet
- QR Code
- Push Payment
- Smart Contracts
Direct entry
The customer enters their card number (or other account number) directly onto the merchant's website.
Things to consider:
- The merchant needs to accept the correct scheme or protocol compared to the customer's account. For example, if the customer has a Amex card and the merchant only supports Visa and MasterCard, the transaction will fail. Often the merchant will display supported schemes and protocols on the checkout before the customer enters their card details.
- The customer should take steps to ensure the security of their account numbers, if the numbers get into the wrong hands they can be used to make transactions fraudulently. Steps include making sure the merchant's checkout is secured by SSL and they don't share their card number to unreputable sources (in fact, I would recommend never sharing your account number anywhere other than a secure online form).
Card-on-file
The customer has previously given the merchant or their partners permission to store their card details. A subsequent checkout is often quicker, more streamlined and more secure so the customer doesn't have to enter their card details again. The stored credentials are used to process the transaction based on the customer's permission to proceed (this is sometimes called a subsequent CIT transaction).
Things to consider:
- The customer may still need to enter their CVV, which adds a little friction
- If your card gets lost or stolen, the customer may need to re-enter their card details with the merchant.
NFC
NFC is built into modern smart phones and devices with secure elements storing a device token representing a payment method. To pay using NFC the customer has to tap their device against an NFC terminal. The devices communicate over NFC and pass appropriatly encrypted device token for use in a payment request.
Things to consider:
- Often a 2nd factor authentication is required on the device, such as FaceID or double-tap, to confirm the payment request
- The combination is generally very secure, even if a fraudster gets their hands on a device token, the whole account is not comprimised as it can be cancelled and reissued without giving the fraudster access to the full card number.
EMV
The EMV is a physical chip protocol embedded into a card for securely communicating the card details between the card and the terminal. A EMV transaction requires a PIN as a 2nd factor authentication.
Things to consider:
- If a fraudster gets hold of the card and the PIN, they can do some damage, so a customer must keep their PIN secure.
Magstripe
Magstripes will soon be a thing of the past. Data is stored in a magnetic strip on the card and read by a card reader for processing.
Things to consider:
- Modern cards should be issued without Magstripe and are replaced with EMV or NFC.
Cheque
Cheque's too are becoming a thing of the past in today's digital world, nevertheless many banks do still issue cheque books upon request. A cheque is essentially a trust based system with personal account details listed (and sometimes even the card number written on the back to guarentee it).
Things to consider:
- If you have a cheque book, I would recommend throwing it away.
Cash
Most modern forms of cash are fiat currencies, meaning it is a government-issued currency that's not backed by a physical commodity such as gold or silver. In terms of using cash, most people understand this one, the customer hands over their cash in exchange for goods and services.
Things to consider:
- Cash is easy to get lost or stolen, so customers need to be careful with their cash
Redirect
After choosing to pay with a method that requires a redirect, the merchant will redirect the customer to the provider and the customer will authenticate and authorize the payment method provider to make the payment.
Things to consider:
- Customers need to keep their passwords secret and should use 2FA if possible
Loyalty Points
Small amounts of loyalty points are earned as a reward for frequent shopping, loyalty program different in how they are redeemed but enough loyalty points could buy a flight or even holiday.
Things to consider:
- Customers need to keep track on whether their loyalty points will expire
Digital Wallets
Similar to NFC payments, Apple, Google and others provide Digital Wallets that allow the customer to tokenise their card and use on an ecommerce checkout instead of entering their card details. It is a more secure method that allows direct communication between the device and merchant, without passing the customers card number.
Things to consider:
- There may be limits to transaction values for digital wallet transaction
QR Code
The customer scans a QR code presented by the merchant to get redirected to their favourite wallet, similar to redirect methods expect often the authentication experience is more mobile-centric and can take advantage of device authentication such as FaceID, etc.
Things to consider:
- Make sure the QR code is from a trusted source.
Push Payment
A push payment is where the merchant provides the customer with their account credentials and the customer performs a transfer from their account to the merchants. Once the merchant has confirmed receipt of the funds, the goods or services are released.
Things to consider:
- Make sure the account details are from a trusted source.
- There may be a delay while the funds are being transferred / confirmed.
Smart Contracts
Web3 Smart Contracts facilitate some exiciting new options for customer <-> merchant agreements.
Things to consider:
- Smart Contracts are still in their early phases and will require an understanding of crypto